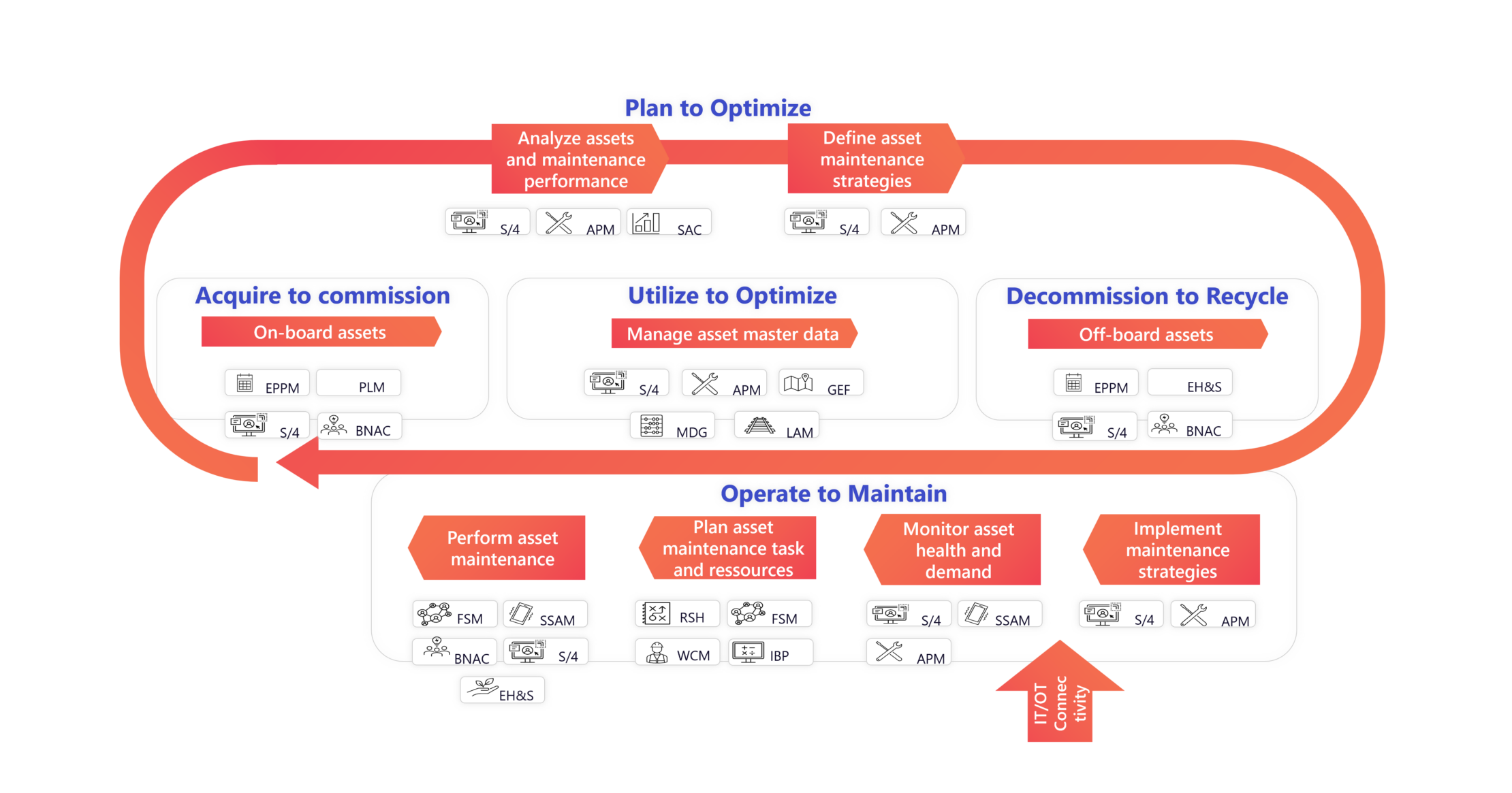
Technical systems are becoming increasingly complex these days. This not only presents challenges, but also opens up significant potential for savings and optimization, particularly in the area of maintenance. In order to do justice to this potential, it is essential to rely on standards and best practice processes that meet the increasing legal requirements and industry standards.
Maintenance plays a decisive role in competition and is a key factor for customer satisfaction. Innovative solutions such as predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs and minimize unplanned downtime, which in turn increases customer satisfaction and security of supply.
Close cooperation between plant operators, manufacturers and maintenance technicians is becoming increasingly important in order to enable automated data exchange. This promotes condition improvement and planning and helps to increase plant availability.
Together we will achieve your goals
By combining the following elements, we create added value for our customers and help them to manage their plants efficiently and effectively: